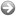The UMD-FBN1
mutations database
Search
Type and number of mutations
This option displays the overall content of the UMD- FBN1 database according to mutation types. You can have access to a specific group of mutations by a simple click on the title (for example to access the list of all missense mutations, click on "Missense").
| All records | Different variants | Samples | |
| 3077 | 1847 | 3044 | |
| 51 | 33 | 50 | |
| 48 | 30 | 47 | |
| 3 | 3 | 3 | |
| 3006 | 1795 | 2974 | |
| 331 | 268 | 331 | |
| 107 | 100 | 107 | |
| 317 | 200 | 317 | |
| 2249 | 1225 | 2225 | |
| 434 | 210 | 434 | |
| 1815 | 1015 | 1793 | |
| 20 | 19 | 20 | |
| 2 | 2 | 2 |
Mutations by exon/intron
This option displays the phasing of the 65 exons of the FBN1 gene. You can have access to small rearrangements localized within one exon (or intron) as well as large rearrangements that include this exon (or intron) by a simple click on the exon (or intron) of interest.
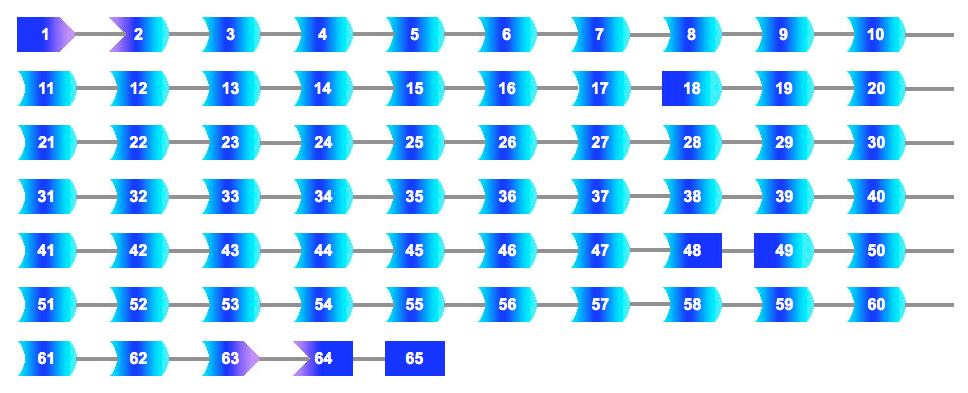
Mutations by protein domains
This option displays the protein domains of the FBN1 protein. You can have access to mutations from one domain by a simple click on the corresponding domain.
Mutations by Phenotype
This table displays the number of record with a specific phenotype. For a better visualisation, only categories are shown, to access sub-categories, click on the +/- button.
I found a mutation
This option allows to search for a specific mutation in order to check if it has been previously reported.
Free search
This option gives access to a quick search and an advanced search interface.
Insertions analysis
Determines for each mutation corresponding to an insertion if repeated sequneces could be involved in the aetiology of this mutation.
Deletions analysis
Determines for each mutation corresponding to a deletion if flanking repeated sequences could be involved in the aetiology of this mutation
UMD-Predictor
The UMD-Predictor system allows to visualize all predictions of the pathogenicity of all nucleotide substitutions from the coding sequence.
Human Splicing Finder
If your mutation is not listed in this database, You can also use the HSF system to evaluate the consequences of substitutions on splicing.